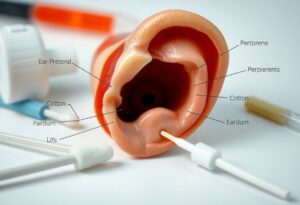
Over time, you may experience issues with your hearing aid that seem perplexing. One common yet often overlooked factor is ceruminous accumulation, or earwax buildup, which can obstruct your device’s effectiveness and create similar symptoms to a malfunctioning hearing aid. Understanding this condition is vital to maintaining your hearing health and ensuring your hearing aid functions optimally, helping you avoid unnecessary repairs or replacements.
Key Takeaways:
- Ceruminous accumulation can obstruct sound transmission, similar to issues caused by a malfunctioning hearing aid.
- Symptoms of cerumen buildup may include muffled hearing and discomfort, which can be mistaken for hearing aid problems.
- Regular ear examinations can help differentiate between ceruminous buildup and hearing aid failures, ensuring appropriate treatment.
The Anatomy of Ceruminous Accumulation
The Role of Earwax in Ear Health
Earwax, or cerumen, serves multiple protective functions, including trapping dust and debris to prevent infections. It also helps maintain a balanced environment in your ear canal by keeping it moisturized, thus reducing the risk of dryness and irritation. This natural lubricant prevents the skin from becoming damaged and creates a barrier against harmful microorganisms.
Mechanisms of Cerumen Production and Removal
Cerumen is produced by sebaceous and ceruminous glands in the ear canal, which secrete a combination of oils and dead skin cells. The natural movements of your jaw while talking and chewing help dislodge and transport earwax out of the canal, ensuring that it does not accumulate excessively. Additionally, the shape of your ear canal aids in the gradual migration of cerumen towards the outer ear, facilitating its removal.
This self-cleaning mechanism typically keeps cerumen levels in check, but alterations due to lifestyle or anatomical factors can disrupt this balance. For instance, excessive use of earphones or cotton swabs can push wax further into the canal, leading to buildup. Your age may also play a role, as cerumen production tends to decrease, resulting in drier, harder wax that is less easily expelled. Understanding these processes can help you maintain optimal ear health and prevent issues associated with buildup.
Symptoms of Ceruminous Build-Up
Key Indicators of Excessive Earwax
Excessive earwax can present with various indicators, including muffled hearing, a feeling of fullness in the ear, and occasional earaches. You may also experience tinnitus, a ringing or buzzing sound in your ear. In some cases, an odor or discharge may accompany these symptoms, signaling a more serious condition that warrants attention.
How Symptoms Parallel Hearing Aid Malfunctions
The symptoms of ceruminous build-up closely mimic those of a faulty hearing aid. For instance, just as a faulty device may distort sound quality or impede audio clarity, excessive earwax can block sound waves, causing muffled hearing. Both scenarios can lead to frustration as communication becomes challenging, prompting an individual to adjust volume settings or reposition devices in an attempt to regain clarity.
Individuals relying on hearing aids often experience sound interruptions or diminished clarity, similar to what occurs with significant earwax build-up. If your hearing aid suddenly fails to deliver clear audio, it could be mistaken for the effects of ceruminous accumulation, leading to unnecessary device adjustments or replacements. Observing these overlaps can help you determine whether a visit to a healthcare professional is necessary to assess potential earwax issues instead of solely attributing problems to hearing aid performance.
Faulty Hearing Aids: Causes and Symptoms
Common Issues with Hearing Aids
Your hearing aid may encounter several common issues that affect performance. Battery failure is frequent, as old or improperly placed batteries can diminish sound quality. Accumulation of dirt or debris can cause blockages, while damaged wires or components might result in intermittent or no sound. Regular maintenance and proper storage can help mitigate these problems.
Recognizing Hearing Aid Malfunctions
You might notice indicators of malfunction, such as distortion or an unnatural amplification of sounds. Difficulty in hearing background noises, sudden drops in volume, or prolonged silence can signal a problem. If you experience these symptoms, troubleshooting your device is necessary to determine the cause and seek appropriate solutions.
For effective troubleshooting, start by checking the battery installation and ensuring it’s charged. Inspect the microphone and receiver for blockages or debris that could impair sound transmission. If sounds are weak, adjusting program settings or cleaning the device may restore functionality. In case issues persist, consulting a professional audiologist is advisable to diagnose technical faults and advice on repairs or replacements.
A Proximity to Misinformation: Similarities between Ceruminous Accumulation and Hearing Aid Problems
How Cerumen Can Mimic Hearing Loss
Ceruminous buildup can lead to hearing challenges that resemble those caused by a faulty hearing aid. When earwax accumulates in the ear canal, it can block sound waves from reaching the eardrum, resulting in muffled hearing or a sensation of fullness. This interference can easily be confused with malfunctioning devices, especially if you’re relying on a hearing aid for enhanced auditory clarity.
Distinguishing Between Wax Build-Up and Equipment Failure
Identifying whether your hearing difficulties stem from cerumen impaction or a malfunctioning hearing aid requires careful evaluation. Observe if symptoms align with recent changes; sudden loss of sound clarity may indicate a faulty device, while gradual changes in hearing might suggest wax buildup. Performing routine checks and cleanings on your hearing aids can also help eliminate equipment failure as the source.
Common signs of cerumen accumulation include a gradual decline in hearing, accompanied by a feeling of blockage in your ear. In contrast, malfunctioning hearing aids often present with intermittent sound disruptions or persistent feedback noise. If your hearing aids are clean and functioning properly but you’re still experiencing issues, it’s wise to consult a healthcare professional to assess for cerumen impaction or to evaluate your devices for faults, ensuring the right course of action is taken.
Diagnostic Tools and Techniques
Medical Examination Methods for Earwax Identification
Your healthcare provider may employ various medical examination techniques to accurately identify ceruminous accumulation. Otoscopy is a common method, using a device equipped with a light and magnifying lens to visualize the ear canal and eardrum. Additionally, imaging tools like tympanometry can evaluate eardrum mobility, while auditory tests may assess hearing impairment linked to earwax build-up. These methods allow for a comprehensive assessment of your ear health.
Troubleshooting Hearing Aids: Best Practices
Regular maintenance of your hearing aids can prevent many issues that mimic earwax blockage. Start by ensuring batteries are charged and connections are secured. Inspect the device for debris or moisture, which can impede performance. Cleaning your hearing aids according to manufacturer guidelines will also enhance sound clarity. If problems persist after basic troubleshooting, consider visiting your audiologist for professional evaluation.
In-depth troubleshooting includes checking for obstructions in the microphone openings and speaker vents, as well as verifying that the charm can’t identify underlying software issues. A simple process involves turning your hearing aids off and on again, which can reset the system. For more complex devices, connecting them to a programming device can help update settings and rectify sound quality. Maintaining a log of the problems you encounter between visits can also aid your audiologist in pinpointing persistent issues effectively.
Treatment Options for Ceruminous Accumulation
Professional Intervention Techniques
Your healthcare provider can employ several professional techniques to safely remove ceruminous buildup. These may include methods like micro-suction, where a small suction device extracts earwax, or curettage, which involves using specialized instruments to scoop out the wax. Both techniques are performed under sterile conditions to minimize risk and ensure your comfort.
At-Home Remedies: Effective or Risky?
At-home treatments for ceruminous accumulation can range from ear drops to irrigation; however, these methods carry potential risks. Over-the-counter earwax softeners might assist with dislodging wax, but using cotton swabs can exacerbate the problem by pushing wax deeper.
While some individuals find success with at-home remedies, caution is warranted. Products such as hydrogen peroxide or saline solutions can break down earwax effectively, but improper use may lead to ear infections or damage to the ear canal. It is advisable to consult a medical professional before attempting any DIY methods, as improper techniques may worsen ceruminous accumulation or complicate an existing condition. Awareness of your ear health and professional guidance helps ensure safe and effective treatment options.
Maintaining Optimal Ear Health and Hearing Aid Functionality
Best Practices for Earwax Management
To prevent ceruminous accumulation, establish a routine for maintaining your ear health. Regularly clean the outer ear with a soft cloth and avoid using cotton swabs, which can push wax deeper. Consider using over-the-counter ear drops specifically designed to soften earwax, and consult your healthcare provider if you notice any significant buildup. Keeping your ears dry after swimming or showering also helps minimize wax production.
Regular Maintenance Tips for Hearing Aids
Hearing aids require consistent care to function optimally. Daily cleaning is vital; wipe down your device with a soft, dry cloth to remove moisture and debris. Replace batteries regularly and check for signs of wear such as excessive wax buildup in the microphone and receiver openings. You might also schedule professional cleanings to ensure thorough maintenance. Thou should keep a log of your hearing aid usage, noting any changes in performance.
- Clean your hearing aids daily with a soft cloth.
- Regularly check and change batteries to ensure reliable performance.
- Keep them dry and protected from extreme temperatures.
- Thou should consider professional servicing every six months for comprehensive maintenance.
Setting a routine can enhance the lifespan of your device. Make a habit of inspecting your hearing aids before and after use to ensure they’re working well. Keeping a protective case when not in use will help prevent damage. Thou should also keep track of any feedback from your hearing aids, such as static or muffled sounds, to address potential issues early.
- Schedule professional cleanings biannually for thorough care.
- Utilize special drying kits designed for hearing aids to prevent moisture-related issues.
- Track performance changes and address them promptly with a specialist.
- Thou must prioritize storing your hearing aids in a safe, dry location when not in use.
Summing up
Ultimately, ceruminous accumulation can closely mimic the symptoms associated with a faulty hearing aid, leading to perceptions of decreased hearing clarity and volume in your auditory experience. If you notice sudden changes in your hearing, it’s vital to consider earwax buildup as a possible cause before assuming your device is malfunctioning. Regular maintenance of your hearing aid, alongside routine ear checks, can help differentiate between device issues and natural earwax changes, ensuring optimal hearing performance.
FAQ
Q: How can ceruminous accumulation be mistaken for a faulty hearing aid?
A: Ceruminous accumulation can block the ear canal, leading to reduced sound transmission, which can resemble the symptoms of a malfunctioning hearing aid.
Q: What symptoms of ceruminous accumulation are similar to hearing aid issues?
A: Symptoms include a decrease in sound clarity, muffled hearing, and the sensation of fullness in the ear, all of which can also occur when a hearing aid is not functioning properly.
Q: How can I differentiate between ceruminous accumulation and a defective hearing aid?
A: Testing the hearing aid with a different device or ensuring the ear is clean can help. If sounds improve after cleaning the ear or changing batteries, it’s likely ceruminous accumulation.
Q: What should I do if I suspect ceruminous accumulation?
A: Consult with a healthcare professional for an evaluation and potential ear cleaning to prevent further issues and restore proper hearing.
Q: Can excessive earwax accumulation affect the performance of my hearing aid?
A: Yes, excessive earwax can interfere with the hearing aid’s microphone and speaker, causing distortion or blockage of sound, thereby mimicking a faulty device.