In This Article
Are you struggling with blocked ears, perhaps feeling a bit muffled or experiencing discomfort? You're not alone. Many people experience earwax build-up, and it can be really frustrating. It's natural to look for solutions, and you might have even come across various manual earwax removal tools online or in shops. But honestly, when it comes to something as delicate as your ears, understanding the right way to approach earwax removal is incredibly important. We're talking about your hearing and overall ear health, after all.
Here at Earwax Removal Devon, we see firsthand the difference safe, professional care makes. This article is all about helping you understand the world of manual earwax removal tools – what they are, how they're used, and crucially, why some are best left to the experts.
What Are Manual Earwax Removal Tools?
Manual earwax removal tools are instruments designed to physically extract earwax from the ear canal. They come in various shapes and sizes, each with a specific purpose. You'll find some of these tools are routinely used by qualified clinicians, while others are marketed directly to consumers for at-home use. And look, that's where things can get a bit confusing, and frankly, risky.
Tools Used by Clinicians
When you visit a professional for earwax removal, they might use a range of specialised manual tools. These aren't just random bits of plastic or metal; they're precision instruments designed for safe and effective removal when used by a trained hand under direct visualisation. Think about it this way: a surgeon wouldn't use kitchen knives, would they? It's the same principle for your ears.
- Curettes: These are small, spoon-shaped instruments, often made of metal or plastic, used to scoop out earwax. They come in various angles and sizes to suit different ear canals and wax consistencies. Clinicians use these with extreme care, gently dislodging and removing wax.
- Jobson Horne Probes: This is a dual-ended instrument, with a loop at one end and a small curette or probe at the other. It's particularly useful for removing softer wax or for gently manipulating wax away from the ear canal walls.
- Ear Picks (Professional Grade): While the term 'ear pick' might sound like something you'd buy in a chemist, professional ear picks are distinct. They are part of a clinician's toolkit, used with precision and always under magnification.
- Manual Irrigation Syringes (Professional Use): While ear irrigation can be done with water, manual syringes are sometimes used by clinicians for controlled water delivery, especially when dealing with stubborn wax that needs softening and flushing. This is different from the bulb syringes you might find for home use, as professional irrigation involves specific techniques and water temperature control to prevent dizziness or ear damage [1].
Tools Sold to Consumers: A Word of Caution
Now, let's talk about the tools you might see advertised for home use. These often look similar to professional instruments, but there's a world of difference in their design, quality, and crucially, the environment in which they're intended to be used. You'll find things like metal ear picks, ear spoons, and even 'ear vacuums' or 'ear cameras' with attached tools. They promise quick fixes, but honestly, they often lead to more problems than they solve.
Why Manual Removal Requires Direct Visualisation
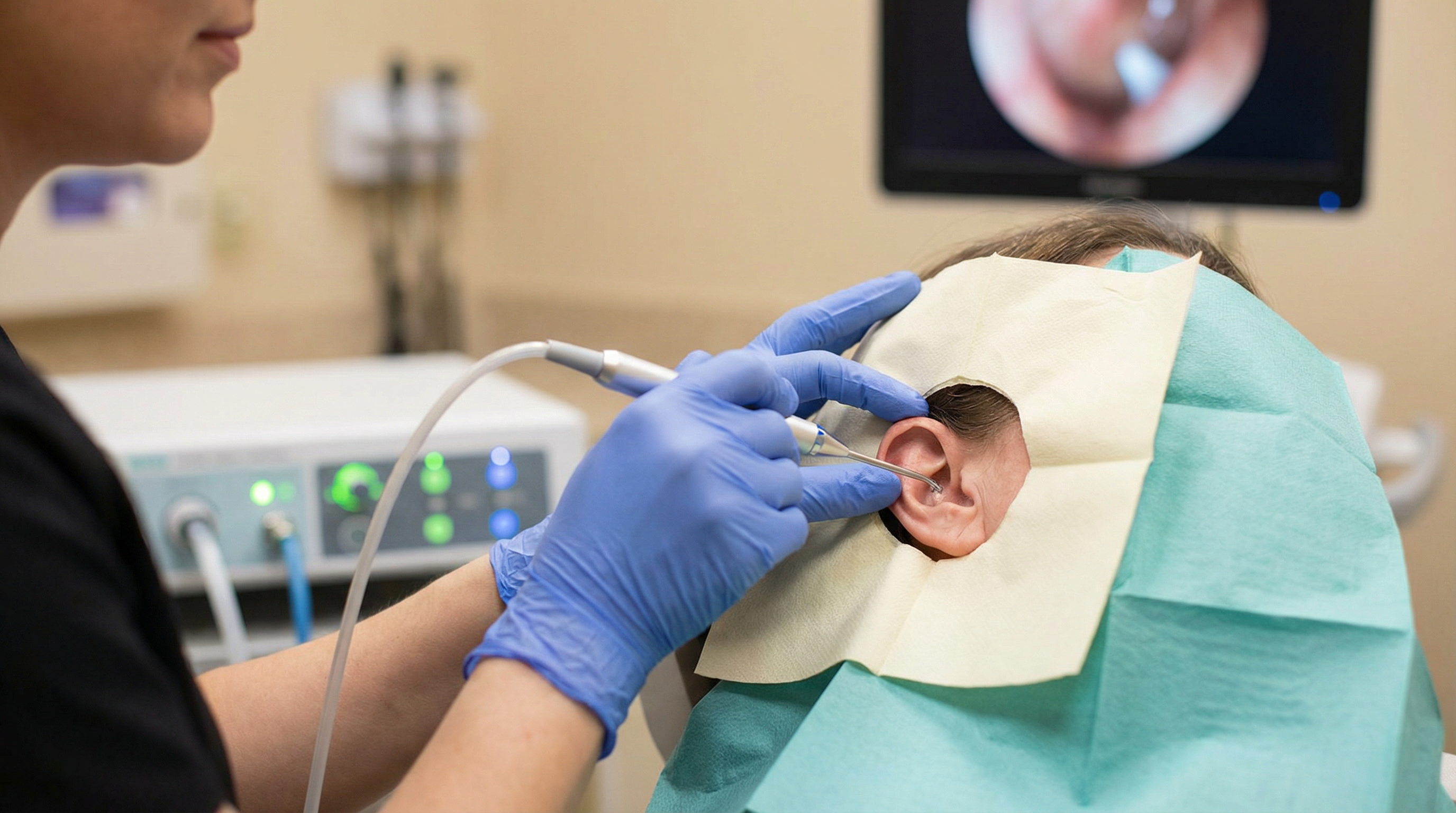
This is a really big point, and it's something we can't stress enough. Professional manual earwax removal, whether it's with curettes or microsuction, always involves direct visualisation. What does that mean? It means the clinician is looking directly into your ear canal, usually with a microscope or an otoscope, to see exactly what they're doing. They can see the wax, the ear canal walls, and your eardrum.
Think about trying to clean something delicate in a dark room, purely by feel. You'd probably cause more damage than good, wouldn't you? That's kind of what you're doing when you try to remove earwax at home without proper visualisation. Your ear canal is curved, the skin is incredibly delicate, and your eardrum is very fragile. Without seeing what's happening, you're essentially working blind.
The Risks of Consumer-Grade Tools and Self-Removal
This is where we get serious, because the risks associated with using consumer-grade tools for self-removal are significant. We've seen the consequences, and they're not pretty. Many people believe they're being careful, but even a slight slip or misjudgement can lead to serious complications.
Canal Laceration
Your ear canal is lined with very thin, sensitive skin. Inserting any object, especially a sharp or rigid one like a metal ear pick, can easily scratch or cut this skin. This is called a canal laceration. Not only is it painful, but it creates an open wound that's ripe for infection. And infections in the ear canal can be really nasty, leading to further pain, discharge, and even temporary hearing loss.
Tympanic Perforation (Perforated Eardrum)
This is perhaps one of the most serious risks. The eardrum (tympanic membrane) is a thin, delicate membrane that separates your outer ear from your middle ear. It's vital for hearing. Pushing a tool too far into the ear canal, or even just accidentally jabbing it, can puncture your eardrum [2]. A perforated eardrum can cause sudden, severe pain, hearing loss, tinnitus (ringing in the ears), and discharge. While some perforations heal on their own, others require surgery, and some can lead to permanent hearing damage.
Wax Impaction and Pushing Wax Deeper
Ironically, trying to remove earwax yourself often makes the problem worse. Instead of removing the wax, you can end up pushing it deeper into the ear canal, compacting it against the eardrum. This is called wax impaction. When wax is pushed deeper, it becomes harder to remove, can cause more significant hearing loss, and increases the risk of discomfort and infection. It's a common issue we see from attempted self-removal.
Other Potential Issues
- Infection: As mentioned, cuts and scratches can lead to bacterial or fungal infections.
- Otitis Externa (Swimmer's Ear): Irritation and trauma to the ear canal can make it more susceptible to this painful outer ear infection.
- Hearing Loss: Beyond perforations, trauma to the delicate structures of the ear can cause temporary or even permanent hearing loss.
- Tinnitus: Damage to the ear can sometimes trigger or worsen tinnitus.
What the Evidence Says About Self-Removal with Manual Tools
The medical community is pretty clear on this: self-removal of earwax using manual tools is generally not recommended. Organisations like the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) and the NHS provide guidance on earwax removal, and their recommendations consistently emphasise professional intervention for impacted or problematic earwax [1] [3].
NICE guideline NG207, which covers earwax removal, outlines various methods including ear irrigation, microsuction, and manual removal, but these are procedures performed by trained healthcare professionals [3]. The guidance doesn't endorse or recommend the use of consumer-grade manual tools for self-removal due to the high risk of complications.
Honestly, the evidence points to a simple truth: leave earwax removal to the professionals. The risks of attempting it yourself far outweigh any perceived benefits.
Clinician vs. Consumer Tools: A Comparison
To make it clearer, here's a quick comparison of professional and consumer earwax removal tools:
| Feature | Professional Manual Tools (e.g., Curettes, Jobson Horne) | Consumer-Grade Manual Tools (e.g., Metal Ear Picks, Ear Spoons) |
|---|---|---|
| User | Trained healthcare professionals (audiologists, ENTs, nurses) | General public, often without training |
| Environment | Clinical setting, sterile conditions | Home environment, often non-sterile |
| Visualisation | Always with direct visualisation (microscope, otoscope) | Typically blind, relying on feel or basic cameras |
| Design | Precision-engineered, medical-grade materials | Variable quality, often mass-produced |
| Risk Profile | Low when performed by trained professional | High risk of injury, infection, and worsening impaction |
| Effectiveness | Highly effective for appropriate wax types | Often ineffective, can push wax deeper |
| Guidance | Supported by clinical guidelines (e.g., NICE NG207) | Not recommended by medical guidelines |
Managing Earwax Safely: What to Expect
So, if you shouldn't be using those home tools, what should you do if you have earwax build-up? The answer is simple: seek professional help. At Earwax Removal Devon, we offer safe, effective, and patient-centred solutions.
Professional Assessment
When you come to us, we'll start with a thorough examination of your ears. This allows us to assess the amount and type of earwax, and to check the health of your ear canal and eardrum. This initial step is really important because it helps us determine the most appropriate and safest removal method for you.
Safe Removal Methods
We primarily use two highly effective and safe methods:
- Microsuction: This is considered the gold standard for earwax removal. It involves using a medical suction device to gently vacuum the wax out of your ear canal. It's performed under direct visualisation using a microscope, meaning we can see exactly what we're doing at all times. It's quick, clean, and generally very well-tolerated. You can learn more about it on our microsuction services page.
- Ear Irrigation: For some types of wax, or if microsuction isn't suitable, we might use ear irrigation. This involves gently flushing the ear canal with warm water to soften and dislodge the wax. Again, this is done using specialised equipment and techniques to ensure safety and comfort. Find out more about this on our ear irrigation services page.
Both of these methods are performed by Eleni, a qualified ear care specialist, ensuring you receive expert care. We'll always discuss the best option for you and explain the process thoroughly.
Don't Take Chances with Your Hearing
Your ears are incredibly important, and they deserve the best care. Trying to remove earwax yourself with manual tools might seem like a quick fix, but the potential for serious damage is just too high. It's not worth the risk of pain, infection, or even permanent hearing loss.
We're here to help you get clear, comfortable ears safely and effectively. Whether you need microsuction, ear irrigation, or just some advice, we're ready to assist. We even offer home visits and emergency appointments across Devon.
Book your appointment with Earwax Removal Devon today. Call us on 01769 302119 or book online at earwaxremovaldevon.com.
References
[1] Ear Care Centre. (2019). Ear Irrigation Guideline. Available at: https://www.earcarecentre.com/uploadedFiles/Pages/Health_Professionals/Protocols/Ear%20Irrigation%20Guideline%202019.pdf [2] Just Ears. (2024). Are Ear Wax Removal Home Kits Safe? Understanding the Risks. Available at: https://www.justears.co.uk/are-ear-wax-removal-home-kits-safe-understanding-the-risks/ [3] National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). (2019). Earwax removal (NG207). Available at: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng207