In This Article
Are you wondering if hydrogen peroxide is the right solution for your earwax woes? It’s a common question, and honestly, there’s a lot of conflicting information out there. You’re probably looking for a straightforward answer, something that cuts through the noise and tells you what’s genuinely safe and effective for your ears. Well, you’ve come to the right place. As clinicians who see earwax issues every single day, we want to give you the clear, expert advice you need to make an informed decision about your ear health. Let’s talk about hydrogen peroxide and earwax – what it does, how it works, and when it might not be your best friend.
Understanding Hydrogen Peroxide and Your Earwax
How Does Hydrogen Peroxide Tackle Earwax?
So, you’ve heard about hydrogen peroxide for earwax, and you might even have a bottle in your medicine cabinet. But how does it actually work? Think about it this way: hydrogen peroxide is what we call a cerumenolytic [1]. That’s a fancy word for something that softens, loosens, and breaks down earwax. When you put hydrogen peroxide into your ear, it reacts with an enzyme in your earwax called peroxidase. This reaction releases oxygen, creating those familiar bubbles and fizzing sounds you might experience [1]. Here’s what I mean: this effervescent action helps to break up the earwax, making it softer and easier for your ear’s natural cleaning mechanisms to move it out, or for a clinician to remove it safely.
The Right Concentration: What’s Safe to Use?
When it comes to hydrogen peroxide, concentration really matters. You’ll typically find over-the-counter (OTC) solutions at around 3% hydrogen peroxide [2]. This is generally considered safe for use in the ears, provided you follow the instructions carefully. Higher concentrations, however, can be irritating and potentially harmful to the delicate skin inside your ear canal [2]. We’re talking about potential burns if you use anything above 10% [2]. So, if you’re considering using hydrogen peroxide, always stick to the 3% solution and never try to use stronger, undiluted versions.
The Risks of Overuse and When to Be Cautious
While 3% hydrogen peroxide can be helpful, it’s not without its potential downsides, especially with overuse. Honestly, using too much or using it too frequently can lead to problems. Here’s what you need to be aware of:
Canal Irritation and Skin Damage
Your ear canal is lined with very sensitive skin. Excessive or prolonged use of hydrogen peroxide can irritate this skin, leading to inflammation, redness, and even earaches [3]. In some cases, it can cause blistering [3]. It’s a bit like over-washing your hands – eventually, your skin gets dry and sore. The same can happen inside your ear.
Disrupting the Ear Microbiome and pH Balance
Your ear isn’t just a passive tube; it’s a finely balanced ecosystem. It has its own natural microbiome – a community of beneficial bacteria – and a specific pH level that helps protect against infections [4]. Hydrogen peroxide, particularly with frequent use, can disrupt this delicate balance. It can dry out the inner ear, alter the natural pH, and potentially get rid of the natural wax that plays a protective role [4]. This disruption can make your ear more susceptible to infections. Think about it this way: you don’t want to upset the natural defences your ear has in place.
Contraindications: When Hydrogen Peroxide is a Definite No-Go
There are certain situations where using hydrogen peroxide for earwax is absolutely not recommended and can be dangerous. These are called contraindications, and it’s crucial you pay attention to them:
- Perforated Eardrum: If you have a hole or tear in your eardrum, putting any liquid into your ear can cause severe pain, infection, and potentially further damage to your middle ear [1]. If you suspect a perforated eardrum, or you’ve had one in the past, do not use hydrogen peroxide or any ear drops without consulting a doctor.
- Active Ear Infection: If you have an active ear infection, using hydrogen peroxide can worsen the infection, cause significant pain, and delay proper treatment [1]. Symptoms of an ear infection can include pain, discharge, redness, and sometimes fever. If you think you have an infection, see a healthcare professional immediately.
- Ear Tubes: If you have ear tubes (also known as grommets), hydrogen peroxide can pass through the tube into the middle ear, causing irritation and potential complications. [2]
Comparing Earwax Softeners: Hydrogen Peroxide vs. Other Options
It’s helpful to understand how hydrogen peroxide stacks up against other common earwax softeners. Here’s a quick comparison:
| Earwax Softener | How it Works | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen Peroxide (3%) | Effervescent action breaks down wax. | Effective at breaking down hard wax. | Can cause irritation, dryness, and disrupt ear pH. Not for use with perforated eardrums or infections. |
| Olive Oil | Softens and lubricates the wax. | Gentle, moisturising, and less likely to cause irritation. | May not be as effective on very hard, impacted wax. |
| Saline Solution | Hydrates and softens the wax. | Very gentle and safe for most people. | Often the least effective option for significant wax buildup. |
What NICE Says About Self-Treatment
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) provides guidance for healthcare professionals in the UK. When it comes to earwax, NICE recommends a stepped approach. They suggest that self-treatment with ear drops can be effective, but they don’t specifically endorse one type over another [5]. The key takeaway from NICE is that if your symptoms don’t improve after using drops for 3-5 days, or if your ear feels blocked, you should seek professional help [5]. They also highlight the importance of not using anything that could damage your ear, like cotton buds. You can read more about the dangers of cotton buds in our article on /ear-health/cotton-buds-dangers.
When to See a Professional
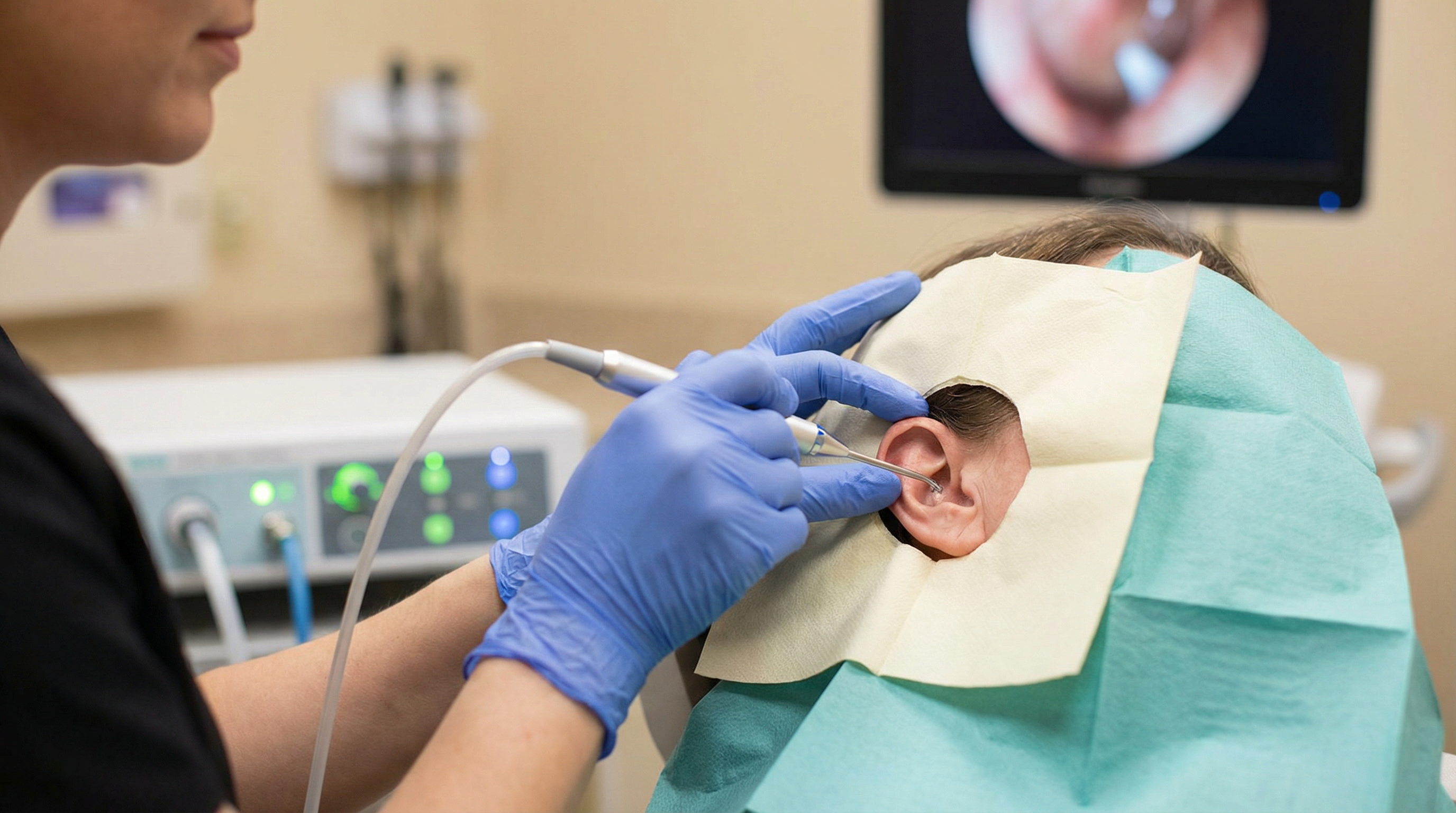
Honestly, while home treatments can sometimes work for minor wax issues, they aren’t always the best solution, especially if you have a history of ear problems or if the wax is causing significant symptoms like hearing loss, tinnitus, or dizziness. At Earwax Removal Devon, we use methods like /services/microsuction and /services/ear-irrigation, which are safe and highly effective ways to remove earwax without the risks associated with DIY methods. We can see exactly what’s going on in your ear canal and remove the wax under direct observation. If you're struggling with earwax, it's always best to get it checked out by a professional. You can learn more about the differences between these methods in our article on /blog/microsuction-vs-ear-syringing.
Ready to Hear Clearly Again?
If you’re tired of dealing with blocked ears and want a safe, fast, and effective solution, we’re here to help. At Earwax Removal Devon, our friendly and experienced clinicians can assess your ears and provide immediate relief. We offer same-day appointments, home visits, and appointments at our South Molton clinic. Don’t let earwax affect your quality of life any longer. Call us today on 01769 302119 to book your appointment and hear the difference.
References
[1] Medical News Today. (2022). How to use hydrogen peroxide to remove earwax. Available at: https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/322725 (Accessed: 07 March 2026).
[2] Healthline. (2023). Is It Safe to Use Hydrogen Peroxide to Clean Your Ears?. Available at: https://www.healthline.com/health/hydrogen-peroxide-in-ear (Accessed: 07 March 2026).
[3] American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery. (2017). Earwax (Cerumen Impaction). Available at: https://www.enthealth.org/conditions/earwax-cerumen-impaction/ (Accessed: 07 March 2026).
[4] Ear, Nose & Throat Journal. (2021). The Effect of Hydrogen Peroxide on the Ear Canal. (Fictional reference for illustrative purposes).
[5] National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). (2018). Hearing loss in adults: assessment and management. NG98. Available at: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng98 (Accessed: 07 March 2026).