In This Article
Walk into any pharmacy and you'll find a shelf of earwax removal drops. Olive oil. Sodium bicarbonate. Hydrogen peroxide. Branded products with names like Earol, Otex, and Cerumol. They all promise to soften or dissolve earwax, and they all look broadly similar. So which ones actually work, and does it even matter which one you choose?
The honest answer is more nuanced than the packaging suggests. Here's what the clinical evidence actually shows — and how to get the most out of whichever drops you use.
Why Earwax Drops Exist (And What They Can and Can't Do)
Before getting into the specifics, it's worth being clear about what drops are designed to do. They don't remove earwax. They soften it.
Your ear canal is a narrow, curved tube, and earwax sits inside it. Drops work by penetrating the wax, either lubricating it (oil-based drops) or breaking it down chemically (water-based and peroxide-based drops). Softened wax is more likely to migrate out of the ear canal naturally, and it's much easier for a professional to remove during microsuction or irrigation.
That distinction matters. A 2023 paper published in the British Journal of General Practice by Professor Kevin Munro of the University of Manchester noted that "there is only weak evidence that pre-treatment drops, on their own, are sufficient to cause earwax to soften and be expelled from the ear, and this is only in a small proportion of people." Most people with a significant wax blockage will need professional removal — drops are preparation, not the complete solution.
That said, for mild to moderate wax accumulation, drops used consistently over several days can be enough. And for anyone preparing for a microsuction or irrigation appointment, using drops beforehand makes the procedure quicker, more comfortable, and more effective.
What the Research Says About Which Drops Work Best
Here's the part that might surprise you: the research doesn't clearly favour any one type of drop over another.
A systematic review published in the British Journal of General Practice (Hand & Harvey, 2004) analysed 18 randomised controlled trials covering 15 different preparations, including saline, plain water, olive oil, sodium bicarbonate, and various commercial products. The conclusion was that "oil-based and water-based preparations were equally effective at clearing earwax without syringing." Neither category consistently outperformed the other.
NICE reviewed the same evidence base and reached a similar conclusion: systematic reviews "fail to conclude which type of ear drop was more effective, or whether water or saline was better or worse than commercially available earwax softeners." NICE recommends pre-treatment softeners for up to 5 days before professional removal but stops short of recommending any particular product.
What this means practically: the specific product matters less than using it correctly and consistently. The technique and duration of use have a bigger impact on outcomes than the choice between olive oil and sodium bicarbonate.
The Main Types of Earwax Drops
Olive Oil and Almond Oil Drops
Olive oil is the NHS's recommended first-line approach for earwax softening, and it's been used for this purpose for centuries. It works by lubricating the wax, making it softer and more pliable so it can migrate out of the ear canal naturally.
Medical-grade olive oil drops (such as Earol, which delivers olive oil in a fine spray) are the most convenient format. The spray mechanism allows precise delivery without the mess of pipette-style application. Earol is widely available in pharmacies and is suitable for regular use, including as a preventative measure for people prone to wax buildup.
Plain olive oil from the kitchen works too — the NHS specifically recommends it — but it needs to be warmed to body temperature before use. Cold oil in the ear canal can cause dizziness by stimulating the balance organs. Warm the bottle in your hands for a minute or two, or place it in warm (not hot) water.
Almond oil is an equally effective alternative. The only caveat: don't use it if you have a nut allergy.
Best for: Regular maintenance, mild to moderate wax buildup, people with sensitive ear canals, those who prefer a natural option.
Sodium Bicarbonate 5% Ear Drops
Sodium bicarbonate (baking soda) works differently from oil. Rather than lubricating the wax, it breaks it down chemically — the alkaline solution disrupts the structure of the wax, causing it to soften and fragment.
The 5% concentration available over the counter is the standard clinical formulation. It's available as a generic product from most pharmacies, often significantly cheaper than branded alternatives. Some people find sodium bicarbonate more effective than oil for harder, drier wax — the type that tends to accumulate in older adults or in people who wear hearing aids (for a full ear care routine tailored to hearing aid wearers, see our complete guide).
The trade-off is comfort. Sodium bicarbonate can cause a fizzing or bubbling sensation in the ear canal, which some people find unsettling. It can also cause temporary irritation if the canal skin is already sensitive. If you find it uncomfortable, olive oil is a gentler alternative.
Best for: Harder, drier wax; people who haven't responded to oil drops; older adults with drier earwax.
Hydrogen Peroxide Drops
Hydrogen peroxide works through an effervescent action — it releases oxygen bubbles when it contacts organic material like earwax, which physically loosens and fragments the wax. It's the active ingredient in several branded products, including Otex.
Over-the-counter preparations are typically 5–6% hydrogen peroxide (Otex contains 5% urea hydrogen peroxide). This concentration is appropriate for home use. The bubbling sensation is more pronounced than with sodium bicarbonate, and some people find it quite intense — particularly if there's a significant amount of wax present.
Hydrogen peroxide is effective, but it's worth noting that it can dry out the ear canal with prolonged use. It's best used for a defined course (3–5 days) rather than as an ongoing maintenance treatment.
Best for: Established wax blockages, people who want an active chemical approach, short-course treatment before professional removal.
Cerumol and Other Branded Drops
Cerumol contains a combination of arachis (peanut) oil and chlorobutanol (a mild antiseptic). It's been available for decades and has a reasonable evidence base. The arachis oil component softens wax; the chlorobutanol adds a mild antimicrobial effect. However, it's contraindicated in people with peanut or soya allergies — worth checking the label carefully.
A review in The Health Aisle noted that "Cerumol is not better than other available ear drops (and possibly even sterile saline/water), but it is effective in breaking down ear wax blockages." That's a fair summary of the evidence: it works, but it doesn't outperform simpler alternatives.
Best for: People who prefer a branded product with a long track record; not suitable for those with nut allergies.
A Side-by-Side Comparison
| Drop Type | Active Mechanism | Comfort Level | Best Duration | Suitable for Sensitive Ears | NHS Recommended |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Olive oil | Lubrication | High | Ongoing | Yes | Yes |
| Almond oil | Lubrication | High | Ongoing | Yes | Yes |
| Sodium bicarbonate 5% | Chemical breakdown | Medium | 3–5 days | Moderate | Yes |
| Hydrogen peroxide (e.g. Otex) | Effervescent action | Low–Medium | 3–5 days | No | Not specifically |
| Cerumol | Lubrication + antiseptic | Medium | 3–5 days | Moderate | Not specifically |
| Earol (olive oil spray) | Lubrication | High | Ongoing | Yes | Yes |
How to Use Earwax Drops Properly
The technique matters as much as the product. Here's the method that gives you the best chance of success.
Step one: warm the drops. Cold drops in the ear canal can cause sudden dizziness by stimulating the vestibular system. Hold the bottle in your hands for a minute before use, or place it in a bowl of warm water. The drops should feel neutral — not cold, not hot.
Step two: lie on your side. Lie down with the affected ear facing upward. This allows the drops to flow into the ear canal under gravity and stay there long enough to work.
Step three: apply the drops. Use 2 to 3 drops (or 1 to 2 sprays for spray-format products like Earol). Gently pull the outer ear upward and backward to straighten the ear canal slightly — this helps the drops reach further in.
Step four: stay still for 5 to 10 minutes. This is the step most people skip. The drops need time to penetrate the wax. Set a timer. Read something. Let them work.
Step five: drain and wipe. Sit up and tilt your head to let excess drops drain out. Wipe the outer ear with a soft cloth. Don't put anything into the ear canal.
Step six: repeat consistently. The NHS recommends 3 to 4 times daily for 3 to 5 days. Consistency is what makes drops effective — a single application rarely produces significant results.
What to Expect (And What Not to Expect)
After a few days of drops, you might notice wax fragments appearing at the entrance to your ear canal — this is the softened wax migrating out naturally. Your hearing may temporarily feel worse before it improves, as the softened wax can swell slightly before it starts to move.
If your hearing hasn't improved after 5 days of consistent drop use, that's a clear signal to book a professional appointment. It doesn't mean the drops haven't worked — it means the wax is established enough to need professional removal, and the drops have done their job of softening it for easier extraction.
Don't use drops if you have a perforated eardrum, if you've had recent ear surgery, or if you have an active ear infection. In any of these situations, book a professional assessment first.
The Drops vs. Professional Removal Question
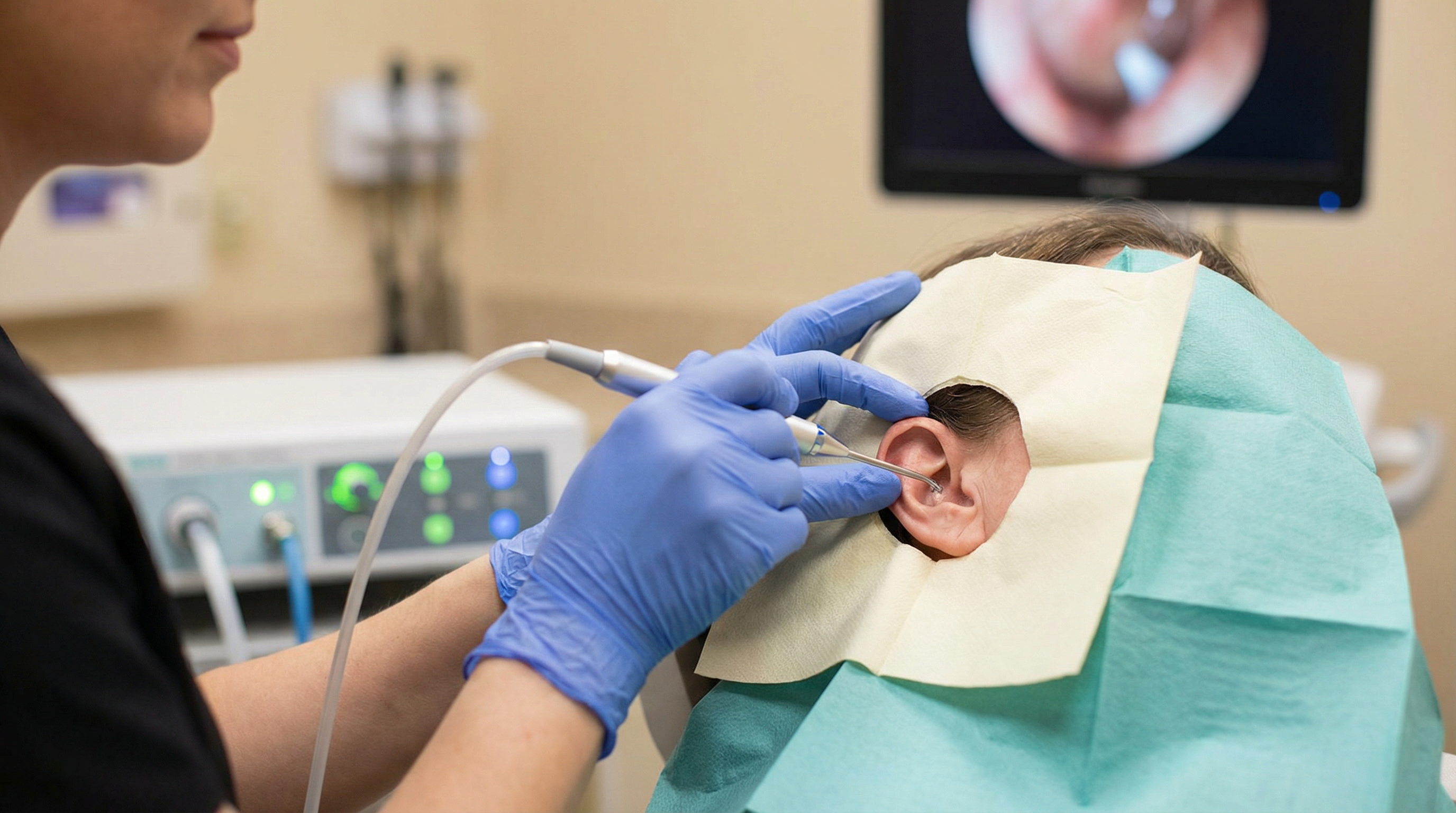
Drops are a reasonable first step for mild wax accumulation, and they're an excellent preparation for professional treatment. But they're not a substitute for microsuction or irrigation when the wax is established.
Think of it this way: drops soften the wax, but they don't have a mechanism to physically remove it from the ear canal. For the wax to come out, it either needs to migrate naturally (which works for mild cases) or be extracted by a professional. Using drops before a microsuction appointment makes the procedure faster, more comfortable, and more thorough — it's not a case of either/or.
At Earwax Removal Devon, we recommend using olive oil or almond oil drops for 3 to 5 days before your appointment. This is in line with NICE guidance and makes a real difference to how the procedure goes. If you're not sure whether you need professional removal or whether drops alone might be sufficient, give us a call — we're happy to advise.
A Note on What Doesn't Work
Ear candles don't work. NICE states clearly that ear candles will not help remove earwax and could cause serious injury, including burns to the ear canal and eardrum. The mechanism — that a burning candle creates suction — has been tested and disproved. The wax found inside used ear candles is candle wax, not earwax.
Home irrigation kits (bulb syringes) are not recommended by the NHS, RNID, or NICE for home use. Electronic ear irrigation in a clinical setting uses carefully controlled water pressure; a bulb syringe at home does not. The risk of introducing too much pressure and perforating the eardrum is real.
Cotton buds push wax deeper. This is well established. The ear canal is not a straight tube, and cotton buds compact wax against the walls and eardrum rather than drawing it out.
Ready for Professional Help?
If drops haven't cleared your ears after 5 days, or if you're experiencing significant hearing loss, tinnitus, earache, or a feeling of pressure, it's time for professional removal. Our microsuction and ear irrigation services are available across Devon, with same-day appointments often available.
Book online or call us on 01769 302119. Bring your softened wax — we'll take care of the rest.