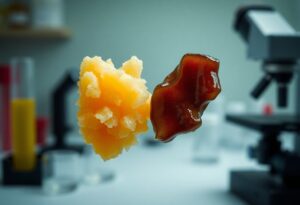
Just as your body has mechanisms to maintain health, your ear canal is designed to clear out wax naturally. You may not realize it, but earwax plays an important role in protecting your ears from bacteria and debris. Understanding how this process works can enhance your awareness of ear health and help you avoid unnecessary interventions. In this post, you’ll learn about the function of the ear canal and the natural ways it protects and cleanses itself.
Key Takeaways:
- The ear canal has a self-cleaning mechanism that helps remove earwax through natural shedding of skin cells and jaw movement.
- Earwax serves protective functions, including trapping dust and debris while preventing infection.
- Interfering with the natural clearing process, such as using cotton swabs, can push wax deeper or cause blockages.
The Anatomy of the Ear Canal
Structure and Length of the Ear Canal
Your ear canal, also known as the external auditory canal, measures approximately 2.5 centimeters in length and has a slightly S-shaped structure. This design not only contributes to sound transmission but also offers protection to the inner ear. Lined with skin and producing earwax, the canal extends from the outer ear to the eardrum, facilitating both auditory mechanics and self-cleansing processes.
The Role of Earwax in Ear Health
Earwax serves a protective function in your ear canal. This natural substance, known as cerumen, traps dust, dirt, and bacteria, preventing them from reaching the eardrum. Additionally, it maintains moisture levels in the canal, preventing dryness and irritation. A healthy balance of earwax ensures your ears remain free from infection while assisting the natural cleaning process.
The composition of earwax varies between individuals and can be influenced by factors such as genetics and environmental exposure. Consisting of a mix of secretions from sebaceous glands, sweat glands, and dead skin cells, earwax can be soft or hard depending on its water content. An optimal quantity not only protects from harmful microorganisms but also facilitates the natural migration of debris out of the ear, ensuring your auditory health is maintained without the need for external cleaning methods.
The Biological Mechanism of Earwax Production
Factors Influencing Earwax Secretion
Your earwax production is influenced by various factors, including genetics, environment, and personal hygiene. These elements can lead to differences in the quantity and consistency of earwax in individuals.
- Genetic predisposition
- Climate and humidity
- Age and ethnicity
- Skin conditions
- Use of earbuds or hearing aids
This variance can affect how well your ears maintain their natural earwax balance.
The Types of Earwax: Wet vs. Dry
You may not realize that there are two primary types of earwax: wet and dry. The consistency and type you have are largely determined by your genetic makeup, with wet earwax being more common among certain populations.
- Wet earwax: sticky and brown
- Dry earwax: crumbly and light-colored
- Genetic factors: influenced by SNPs
- Environmental impacts: sweat and skin composition
- Variations across populations: prevalence differences
Assume that cultural and environmental factors also play a role in the earwax type present in different regions.
| Type of Earwax | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Wet Earwax | Sticky, dark, and more common in individuals of African or European descent |
| Dry Earwax | Flaky, light-colored, more prevalent among East Asian populations |
| Genetic Influence | Determined by specific genes, notably ABCC11 |
| Environmental Factors | Humidity and lifestyle can alter wax consistency |
| Health Implications | Earwax type may relate to certain skin and health conditions |
Your understanding of the differences between wet and dry earwax can be valuable in recognizing potential ear health issues. The genetic makeup plays a significant role in determining your earwax type, which can affect how your ears naturally cleanse themselves. This can impact personal hygiene practices and even provide insight into your overall health.
- Earwax and hygiene correlation
- Potential health implications
- Environment’s role in consistency and production
- Variability in earwax types among demographics
- Awareness for personal ear care
Assume that understanding these types will enhance your knowledge of proper ear care techniques.
The Natural Cleansing Process of the Ear Canal
How Movement Aids Earwax Removal
Your ear canal benefits from movement, which aids the natural removal of earwax. Activities such as chewing or speaking stimulate the surrounding muscles, creating vibrations that help dislodge and transport wax toward the outer part of the ear canal. This process ensures that earwax doesn’t accumulate excessively, maintaining a healthy ear environment.
The Role of Jaw Movement and Swallowing
Jaw movement and swallowing play significant roles in maintaining ear health. These actions engage muscles that create a gentle pumping effect, naturally pushing earwax toward the entrance of the ear canal. By incorporating these movements into your daily routine, you support your ear’s self-cleaning abilities effectively.
As you chew or swallow, the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) flexes, which exerts pressure on the surrounding tissues, including the ear canal. This rhythmic motion not only promotes the movement of earwax but also encourages the shedding of dead skin cells within the canal. Regularly performing these activities can help minimize blockages and maintain a clear ear canal, reducing the need for manual cleaning or interventions.
Environmental Impact on Earwax Dynamics
External Factors Affecting Wax Build-Up
Your earwax production can be influenced by various external elements. Factors such as pollution, dust, and allergens can irritate the ear canal, prompting increased wax secretion. Other influences include your occupation and lifestyle, which may expose you to different irritants. Additionally, the use of earplugs or headphones can alter the natural wax clearing mechanism. You may notice a change in your earwax consistency or volume due to:
- Environmental pollutants
- Climate conditions
- Occupational hazards
Thou should be aware of your surroundings.
The Role of Humidity and Climate
The climate you live in plays a significant role in earwax dynamics. Humid environments often lead to a softer and more fluid type of earwax, while dry climates encourage harder wax formation. When humidity levels are high, your body tends to produce wax that is less likely to cause blockage, promoting efficient natural cleansing. In contrast, those in arid regions may find their earwax prone to drying out and compacting, potentially leading to impaction and discomfort. Adjusting your ear care routine based on climate can help maintain optimal ear health.
Common Misconceptions about Earwax Removal
Debunking Myths Surrounding Q-tips and Ear Cleaning
Many believe Q-tips are effective for ear cleaning, but they often push wax deeper into the ear canal, leading to blockages rather than removal. Using them can also cause irritation or injury to the sensitive skin inside your ear.
- They create a false sense of cleanliness.
- Frequent use can lead to impacted wax.
- The ear canal cleans itself effectively.
The misconception that you need to clean your ears frequently can lead to unnecessary complications. Over-cleaning can disrupt the natural balance of earwax production, prompting the glands to work overtime. This can result in increased wax buildup, necessitating professional removal. Additionally, overzealous cleaning methods may cause abrasions or infections, underscoring the need for a balanced approach.
The Risks of Over-Cleaning
Over-cleaning your ears not only interferes with your body’s natural processes but also poses serious health risks. The ear canal’s delicate skin can become damaged or infected from excessive manipulation, and the potential for introducing bacteria increases significantly. Regular cleaning can lead to chronic issues such as ear infections, pain, or even hearing loss if wax is excessively removed, disrupting the protective barrier that earwax provides.

When to Seek Professional Help
Warning Signs of Earwax Impaction
If you experience symptoms such as hearing loss, earache, a feeling of fullness in the ear, or persistent itchiness, these may indicate earwax impaction. Discomfort that doesn’t resolve on its own or the presence of fluid leaking from your ear also signals a potential blockage. Promptly recognizing these signs helps prevent further complications and keeps your auditory health in check.
Medical Interventions for Earwax Removal
In instances characterized by severe blockage or recurring issues, healthcare professionals may utilize several methods for earwax extraction. Options include suctioning, irrigation, or the use of specialized instruments to gently remove the impaction. You might also receive medications to soften the wax prior to the procedure, enhancing the effectiveness of the intervention.
Typically, a healthcare provider assesses your condition before choosing a method for earwax removal. For instance, suctioning is often preferred for its precision, especially in cases where the ear canal is sensitive. Alternatively, irrigation might involve a warm saline solution to flush out the wax. These interventions not only alleviate discomfort but also restore proper auditory function, ensuring that your ears remain healthy and clear of obstructions.
Best Practices for Ear Hygiene
Strategies for Maintaining Ear Health
Regularly cleaning the outer ear with a soft cloth helps prevent the buildup of dirt and oil, reducing the risk of infection. You should avoid inserting objects into the ear canal, as this can push wax further in and create impaction. Schedule annual check-ups with your healthcare provider to monitor ear health, especially if you frequently use earplugs or headphones.
Natural Remedies and Home Care Tips
Using natural oils such as olive or almond oil can soften earwax, making it easier for your body to expel it naturally. Warm a few drops slightly and place them in your ear to help with wax expulsion. Additionally, staying hydrated and using a humidifier can contribute to healthy ear function. Thou should consider incorporating gentle steam inhalation to maintain clear ears, particularly during cold seasons.
- Apply a few drops of warm olive oil weekly for natural softening.
- Use a bulb syringe with saline solution for gentle rinsing.
- Remain hydrated for optimal ear health.
- Employ steam inhalation to clear sinus and ear blockages.
- Thou can also explore herbal remedies like garlic oil for infection prevention.
Maintaining ear health can be enhanced through easy home care routines. Applying diluted hydrogen peroxide can also help in softening and safely removing earwax. Ensure the mixture is not too strong and consult with a healthcare professional if you experience irritation. Regular monitoring of ear health can also prevent larger issues from developing, allowing your body to function without blockage. Thou should remain vigilant about any changes in hearing or discomfort.
- Consider using a few drops of hydrogen peroxide as a wax softener, with caution.
- Incorporate gentle massage around the ear area to promote circulation.
- Try ear drops formulated from natural ingredients for occasional use.
- Consult healthcare providers before trying new remedies.
- Thou may wish to observe any unusual symptoms and adapt your care accordingly.
The Future of Earwax Management
Innovations in Ear Health Products
Advancements in ear health products are reshaping how you approach earwax management. Devices like smart ear-cleaning tools utilize gentle suction technology to remove wax safely, while ear drops containing natural enzymes are designed to soften and dissolve wax efficiently. Many new products emphasize user-friendly designs and effective ingredients, allowing you to maintain ear hygiene with minimal effort and discomfort.
Evolving Perspectives on Ear Care
Understanding ear care is shifting towards prioritizing natural bodily functions over invasive procedures. You may find that education around earwax benefits is becoming more widespread, encouraging a hands-off approach unless absolutely necessary. This paradigm promotes awareness about how earwax protects against dirt and bacteria, ultimately advocating for minimal intervention to maintain ear health.
As awareness increases, medical professionals and consumers alike are recognizing the limitations of traditional cleaning methods. Scientific studies highlight the body’s ability to manage earwax naturally, suggesting that routine cleaning may not be necessary for everyone. You may find conversations centered around the importance of listening to your body rather than adhering to outdated habits, changing the way you think about ear health and maintenance.
Summing up
Hence, understanding the ear canal’s natural mechanisms to clear wax empowers you to manage your ear health more effectively. As you appreciate how earwax protects and lubricates your ears, you’ll recognize that your ears typically self-clean through movements like chewing or talking. By avoiding unnecessary cleaning methods or cotton swabs, you allow your ear canal to maintain its balance and function. Staying informed about these processes ensures you take responsible steps in maintaining your auditory health.
FAQ
Q: What is the ear canal and its function?
A: The ear canal is a tube-like structure that runs from the outer ear to the eardrum. Its primary function is to carry sound waves to the eardrum while also protecting the inner ear from debris and pathogens.
Q: How does the ear canal naturally clear wax?
A: The ear canal naturally clears wax through a process called migration. The skin in the canal continuously sheds and regenerates, helping to push earwax (cerumen) towards the opening, where it can exit the ear or be washed away.
Q: What is earwax, and why is it important?
A: Earwax, or cerumen, is a natural substance produced by glands in the ear canal. It serves to lubricate and protect the ear by trapping dust, debris, and microorganisms, preventing them from reaching the eardrum.
Q: Are there risks associated with earwax buildup?
A: Yes, excessive earwax buildup can lead to blockage, resulting in symptoms like hearing loss, discomfort, and infections. It’s important to monitor earwax levels and seek professional help if severe buildup occurs.
Q: How can one safely manage earwax at home?
A: One can manage earwax at home by using a damp cloth to clean the outer ear and avoiding cotton swabs, which can push wax deeper. Over-the-counter ear drops may also help soften wax for easier natural removal.